What is Cyber Security?
The term ‘cyber security’ refers to all safeguards and measures implemented to reduce the likelihood of a digital security breach. Cyber security affects all computers and mobile devices across the board –all of which may be targeted by cyber criminals.
Cyber security focuses heavily on privacy and confidentiality, along with data integrity and identity protection. Security breaches in general are nothing new, but have become more commonplace and problematic in today’s digital era. The greater the extent to which the world becomes reliant on connected technology, the greater the threat posed by cybercriminals worldwide.
From reputation damage to system downtime to financial loss, cyber security issues can be incredibly costly. According to a recent study, almost half of all businesses operating in 2017 experienced at least one cyber attack or attempted security breach. Precisely the reason why businesses worldwide have begun prioritizing cyber security, implementing robust protective measures and hiring cyber security experts to oversee their operations.
The Importance of Security
The Internet has transformed the face of everyday life for billions of people worldwide. Already
enormous, daily web traffic volumes are growing at an exponential rate. To such an extent that the vast majority of communications and business activities worldwide are fundamentally reliant on the Internet. From simple retail purchases to the most sensitive and high-profile business activities, everything takes place online. All of which adds up to a near-irresistible opportunity for the 21st century cyber criminal.
Turning a blind eye to cyber security is no longer an option. Businesses that fail to adequately protect themselves face the prospect of catastrophic consequences. Irrespective of the size, nature or purpose of the business, the effects of a cyber attack can be devastating. What’s more, some of the highest-profile attacks over recent years have demonstrated how even the biggest companies in the world aren’t always as well protected as they think they are. Even when their systems are brought back online and business continues as normal, the reputational damage incurred can be much more difficult to overcome.
Of course, it’s not simply a case of proactively protecting your business and its general interests from cyber attacks. You also need to think carefully about the extent to which your customers are protected. Oftentimes, a security breach that has negative consequences for one or more customers can be far more detrimental than an attack on the company itself.
Businesses aren’t simply expected to protect their customers online – they have a legal obligation to do so. All of which amounts to yet another responsibility, which calls for the input and expertise of talented of cyber security specialists.
Insiders and Outsiders
As far as general data security is concerned, there are two classifications of people – insiders and outsiders (aka employees and non-employees). three classes of computer security and crime caused by each of the two types, plus a special class of threats that are not directly caused by humans, namely accidents.
The seven individual classes are as follows:
1. Insiders overt. Overt actions on the part of insiders are usually the work of dissatisfied
employees, often resulting in data being compromised and equipment being destroyed.
2. Insiders covert. Employees within a company can inflict more serious damage than outsiders,
due to their access privileges and extensive knowledge of the organization in general.
3. Insiders unintended. Many security issues or threats that occur internally are the result of
nothing more than genuine human error. This being one of the most common threat classes.
4. Outsiders overt. Direct attacks on network systems and computer facilities by outsiders, which also incorporates DoS attacks.
5. Outsiders covert. This refers to the type of attack that involves transmitting rogue software to one or more computers or systems from outside the business.
6. Outsiders unintended. It is fairly rare that an outsider will harm a computer or access sensitive data unintentionally.
7. Accidents. Issues regarding data integrity or security can arise due to unpredictable accidents that cannot be prevented, such as natural disasters, workplace fires and so on.
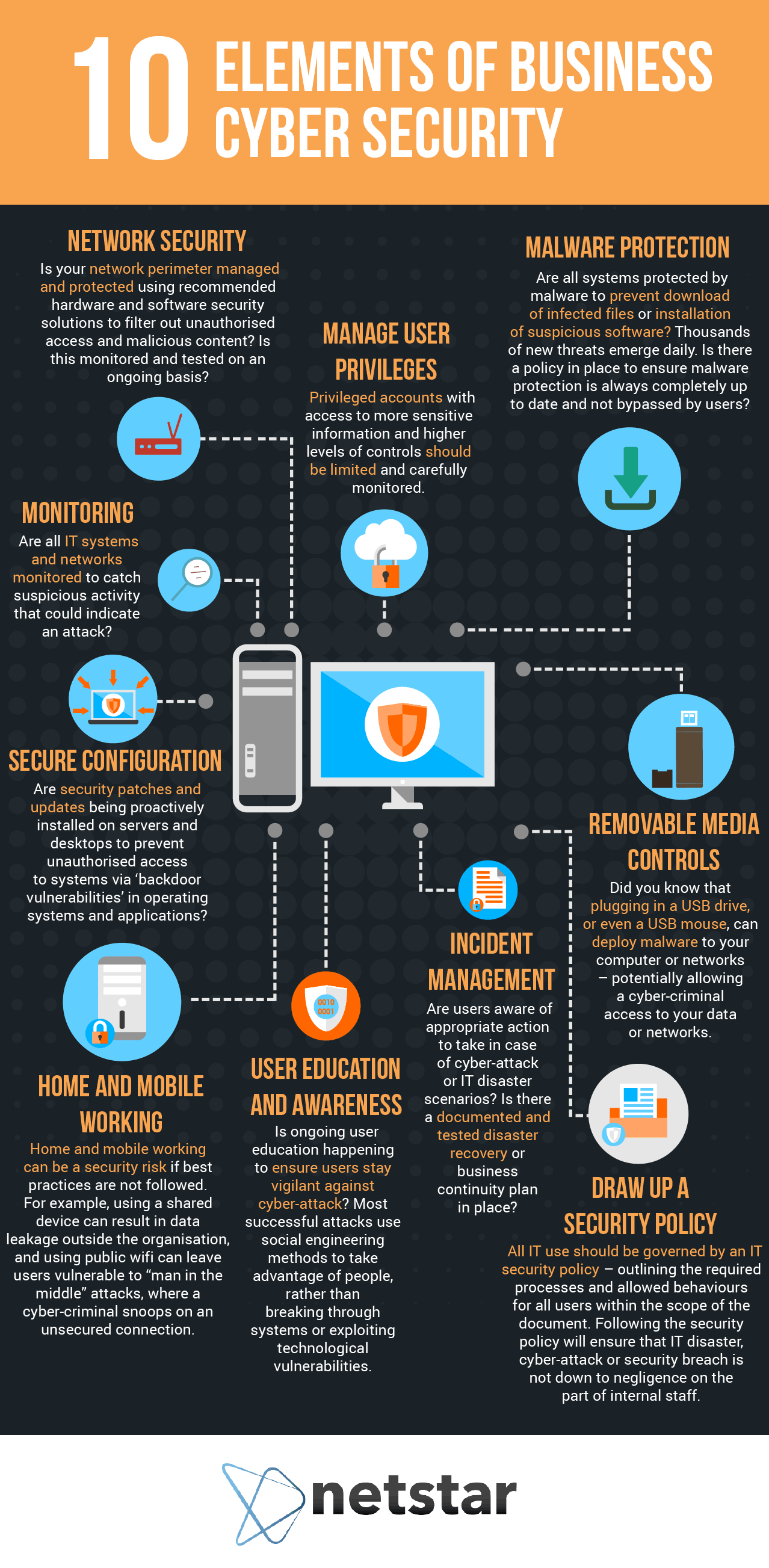
Microsoft’s 10 Laws of Cyber Security
Leading software companies like Microsoft employ enormous teams of cyber security experts tosafeguard their systems and software. Over the years, Microsoft has published an extensive archive invaluable cyber security guidelines for businesses of all shapes and sizes. They’ve also produced and published their own “10 laws of cyber security”, which can and should be implemented at all levels throughout the business.
The 10 rules outlined by Microsoft are as follows:
- If someone can persuade you to run their program on your computer, it’s not your computer
anymore. - If someone can alter the operating system on your computer, it’s not your computer anymore.
- If someone has unrestricted physical access to your computer, it’s not your computer anymore
- If you allow someone to upload anything it’s a to your website, it’s not your website anymore.
- Weak passwords defeat strong security.
- A computer is only as secure as its owner/user is trustworthy.
- Encrypted data is only as secure as the decryption key.
- An out-of-date virus scanner is only marginally better than none at all.
- Absolute anonymity isn’t practical, in real life or on the Web.
- Technology is not a panacea.











Informative
thank you keep visitng